Matrix Management Wiki
Home » The Productivity Key » 4J. Standardization
- 4J1. Standardization of methods and processes allows individuals or teams to work together more efficiently.
- 4J2. VM 1.0 standardized methods:
- 4J2i. Most work is managed by the individual, and so each person has his own method for making decisions, solving problems, or planning a project.
- 4J3. MM 2.0 standardized methods:
- 4J3i. Most work is managed by teams, and the professionals who sit on those teams often participate in multiple teams; therefore, the organization needs to standardize methods that will be used across teams.
- 4J3ia. The processes for managing the work need to be collaborative, as MM 2.0 is based on collaborative leadership (see Section 7). Therefore, the methods teams use to plan, make decisions, and solve problems need to be collaborative.
- 4J3ib. Since people usually sit on multiple teams, they need to be able to use the same set of methods and tools from one team to the next if teams are to be productive.
- 4J4. Standardized processes:
- 4J4i. Another aspect of standardization is standardizing the steps within a process to make projects and business processes more repeatable.
- 4J4ia. Business processes that are repeatable have less risk and are more efficient.
- 4J4ib. Most projects that are done repeatedly use the same technical processes to produce the deliverable, which should be standardized. This makes the projects less risky and more efficient.
- 4J4ic. Figure 4.1. Repeatable processes for business processes and projects.
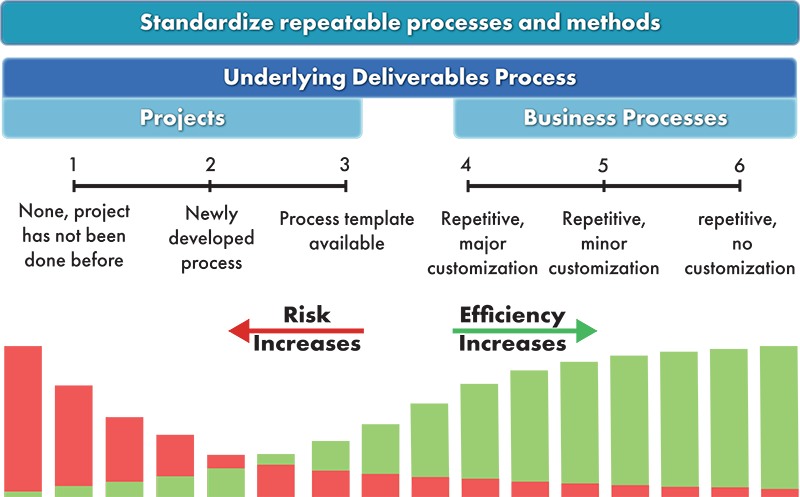
- 4J5. The benefits of using standardized collaborative methods and repeatable processes:
- 4J5i. By having common methods and repeatable processes, people have a common base to work from and work together more easily.
- 4J5ii. Standardized methods and processes should be based on best practices—either developed from the inside or brought in from the outside. Deploying best practices reduces risks because people use proven methodologies rather than something they made up on the spot.
- 4J6. Focus creativity on running the business:
- 4J6i. By having standard methods and mapped processes in place, teams don’t have to reinvent the wheel every time they approach a new situation—they already have a toolbox in place. Therefore, they don’t waste their creativity on reinventing tools that already exist. Instead, they can apply their creativity to the work itself: engineering the new widget, coding the next application, creating a new marketing plan.
- 4J6ii. Practices that are not core to the business are best brought in by outside sources whose business is the development of those practices.
- 4J6iii. Standardized methods and processes should promote and not stifle individual creativity.

